Native Applications
Native apps are mobile apps specifically designed and built for one particular operating system, like iOS or Android. They use the programming languages that are standard for that platform, such as Swift or Objective-C for iOS, and Java or Kotlin for Android. Because they’re made just for one OS, native apps can take full advantage of the unique features and tools the platform offers, resulting in better performance and a smoother user experience.
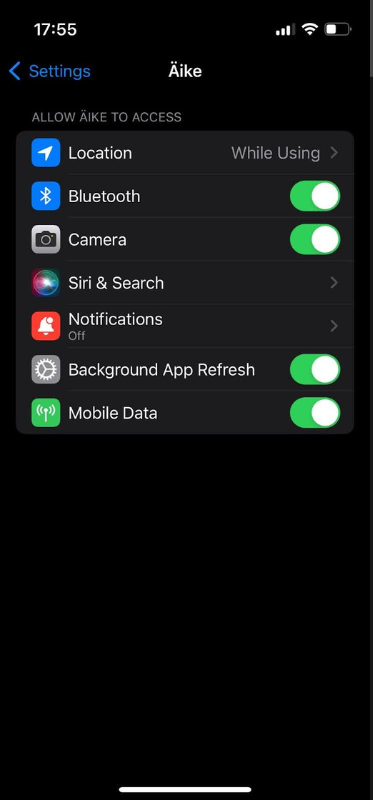
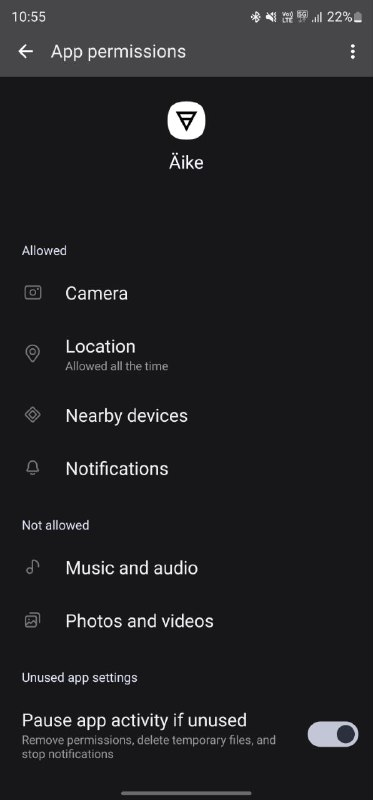
One of the main benefits of native apps is their ability to work closely with the device’s hardware and software. This means they can directly access features like the camera, GPS, microphone, and sensors, which allows for richer functionalities. For example, native apps can take high-quality photos, offer precise location services, or support advanced features like gaming and augmented reality with great responsiveness.
Native apps also benefit from being able to use platform-specific design elements and UI components, which helps create a user experience that feels familiar and intuitive. They typically get updates and support more easily since they follow the platform’s standards and can quickly adopt new features when the OS is updated.
However, a downside is that developing native apps for both iOS and Android requires separate codebases, which can be more resource-intensive and costly. Despite this, many businesses choose native apps because they provide high performance and a top-notch user experience.
For example, as a native app, Waze can make the most of the device’s features, like GPS for real-time navigation and location-based services. This means it can deliver precise navigation and traffic updates even when you're not actively using the app. It also integrates smoothly with other phone functions, such as notifications. This native design helps Waze offer a quick and effective user experience, which is essential for providing up-to-date traffic information and directions.